Carrying Baggage Through Query Plans: Why Wide Queries Get Heavy
Learn why SQL Server execution plans carry too many columns through expensive operations like sorts and hash joins, causing memory grants and slow query performance. Discover two techniques to optimize wide queries using temp tables and derived tables.
Resulting Data Types from Union Operations – Andy Brownsword
The UNION and UNION ALL operators allow us to combine results, but there’s no guarantee that each set of results uses the same data types. So what data types are returned?…
Best Practices for Docker to run SQL Server on a Mac
Check out this consolidated list of things you can (or should) do when using Docker to run SQL Server on a Mac.
A Little About Index Design Patterns In SQL Server – Darling Data
The SQL Server green index suggestion is great for the where clause, but doesn't take into account sort by, group by, etc.
SQLite import with AutoCommit turned off - ETOOBUSY
Until I came to read Schwern’s little gem, hinting to turn AutoCommit off. That hit the nail so good that one single hit sufficed.
Text::CSV_XS is extremely fast, using that to handle the CSV should take care of that side of the performance problem.
There should be no need for special bulk insert code to make DBD::SQLite performant. An insert statement with bind parameters is very fast. The main trick is to turn off AutoCommit in DBI and do all the inserts in a single transaction.
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/15331791/dbicsv-implementation-based-on-sqlite/15337369#15337369
Sereal — a binary data serialization format | by booking.development | Booking.com Engineering | Medium
By: Steffen Müller, Yves Orton, Damian Gryski, Chris Veenboer, Rafaël Garcia-Suarez, Ævar Arnfjörð Bjarmason As with many things in computing, serialization of data structures is a game of…
SQL users: The QUALIFY clause is pure syntactic sugar
https://modern-sql.com/caniuse/qualify
Using a window function, we could add in a new column total_order_amount which represents the total order amount per customer. We could simply write:
SELECT
date,
customer,
order_amount,
SUM(order_amount) OVER(PARTITION BY customer) AS total_order_amount
FROM orders
ORDER BY datethe window function SUM(order_amount) OVER(PARTITION BY customer) effectively partitioned our table into different “windows” (one for each customer) and then calculated the total_order_amount for each of these windows. All of this was achieved without using a GROUP BY aggregation, allowing us to retain the same number of rows.
Different SQL TimeStamp functions in SQL Server
This article will show different SQL timestamp functions available with examples
Learn SQL: User-Defined Stored Procedures
Stored procedures are one more powerful object we have at our disposal. They can help us handle many tasks, and improve performance and security.
DROP PROCEDURE IF EXISTS p_customer_all;
GO
CREATE PROCEDURE p_customer_all
-- procedure returns all rows from the customer table
AS BEGIN
SELECT *
FROM customer;
END;
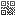
Random Date Generator in SQL Server
In this article we look at how to generate random dates in SQL Server to build a sample dataset along with code and examples.
SELECT DATEADD(DAY, RAND(CHECKSUM(NEWID()))*(1+DATEDIFF(DAY, @StartDate, @EndDate)),@StartDate) AS 'SalesDate';CHECKSUM(NEWID()) is the salt for the rand() function
NEWID() generates a random unique ID for a row. Ordering by NEWID() will randomly order query results. Adding a TOP statement will return a finite number of random rows. For example, to get 10 random rows from a table:
SELECT TOP 10 *
FROM tablename
WHERE condition
ORDER BY NEWID()Best Practices for Writing Good SQL Code
5. Modularize Code with Common Table Expressions
CTEs create a temporary table that allow you to “query a query.”
https://www.essentialsql.com/introduction-common-table-expressions-ctes/
The advantage of a CTE (your second statement) over a derived table is that they can reference themselves and be used for recursion.
with avg_female_salary as (
SELECT AVG(salary) as avg_salary
FROM salaries
WHERE gender = "Female"
)
SELECT name, salary
FROM People
WHERE salary >= (SELECT avg_salary FROM avg_female_salary)7. Simplify Code using Temporary Functions
https://cloud.google.com/bigquery/docs/reference/standard-sql/user-defined-functions
CREATE TEMPORARY FUNCTION seniority(tenure INT64) AS (
CASE WHEN tenure < 1 THEN "analyst"
WHEN tenure BETWEEN 1 and 3 THEN "associate"
WHEN tenure BETWEEN 3 and 5 THEN "senior"
WHEN tenure > 5 THEN "vp"
ELSE "n/a"
END
);
SELECT name
, seniority(tenure) as seniority
FROM employeesMax Maischein. What I learned about SQL in 2018
PerlCon 2019 Rīga — Day 2 — 8 August 2019
~20:00 - Window functions
~33:45 - CTE
~43:00 - Recursive CTE
This talk shows how to use SQL Window Functions (ISO SQL:2008) and how to use Common Table Expressions (CTE, ISO SQL:1999).
Using these two techniques, you can often avoid munging the query result afterwards. This potentially saves roundtrips between the program and the database.
The presentation assumes an intermediate familiarity with SQL. To get the most of the presentation, youshpuld be familiar with SELECT and JOIN. The Perl level is suitable for the beginner, but there will be very little Perl.
5 Window Function Examples to Take Your SQL Skills to the Next Level
What are Window Functions?
Window functions are functions that perform calculations over multiple rows of the dataset while maintaining the same rows and row count of the original table.
10 Quick SQL Tips After Writing Daily in SQL for 3 Years
4. CTE > Sub-queries
In most situations you want to use a CTE (common table expression) instead of a sub-query.
5. Using SUM and CASE WHEN Together
select
sum(case when allergies = 'Penicillin' and city = 'Burlington' then 1 else 0 end) as allergies_burl
, sum(case when allergies = 'Penicillin' and city = 'Oakville' then 1 else 0 end) as allergies_oak
from patientsStart where clause with true
where 1=1
and ...
and ...
and...
7. Don’t Forget About Window Functions
select
p.*
, MAX(weight) over (partition by city) as maxwt_by_city
from patients pWindow functions are a great way to keep all of the data rows and then append another column with important aggregate details.
Tune and Optimize SQL Server Queries
In this article we look at things you should know to help tune and optimize your SQL Server queries.
- Always Check the Execution Plan
- Find the Operators that have Highest Cost
- Look for Warnings
- Arrows Between Operators Provide Good Insight
- Execution Plan Properties Window
- Index Suggestions
Rebuild all SQL Server Indexes for all Tables in all Databases
In this tip we look at a simple script you can use to rebuild all SQL Server indexes for all specified databases.
SET @cmd = 'ALTER INDEX ALL ON ' + @Table + ' REBUILD'
--PRINT @cmd -- uncomment if you want to see commands
EXEC (@cmd)
How to use INFORMATION_SCHEMA Views in SQL Server
INFORMATION_SCHEMA Views allow you to find what tables are in your schema.
Search for varchar(max) and nvarchar(max)
select * from INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS
where CHARACTER_MAXIMUM_LENGTH = -1
Questions About Pivoting Data in SQL Server You Were Too Shy to Ask - Simple Talk
Of all the basic SQL operations, the pivot seems to cause the most problems. We can tell from the way that old articles on Simple-Talk on the topic continue to be read. It turns out that there are several questions that come to mind while learning about pivoting, but which are seldom asked on forums. Once more, Robert Sheldon attempts to answer these unspoken questions.
How to Get NULLs Horribly Wrong in SQL Server - Simple Talk
NULLs in SQL are a mixed blessing. The Three-Valued Logic of SQL has its uses but can cause difficulties to anyone who assumes that NULL has a 'value'. It can make reports go horribly wrong in a number of alarming ways, as Robert Sheldon explains.
6 SQL Queries Every Data Engineer Should Be Aware of
Running Totals
SELECT id,month
, Amount
, SUM(Amount) OVER (ORDER BY id) as total_sum
FROM billCommon Table Expressions
WITH idtempp as (
SELECT id as id
FROM id
WHERE country = "US"
AND status = "Y"
)
SELECT *
FROM bill
WHERE id in (SELECT id from idtempp)Temporary Functions
Temporary functions allow you to modify the data easily without writing huge case statements.
CREATE TEMPORARY FUNCTION get_gender(type varchar) AS (
CASE WHEN type = "M" THEN "male"
WHEN type = "F" THEN "female"
ELSE "n/a"
END
)
SELECT
name,
get_gender(Type) as gender
FROM bill